| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 |
- FutureBuilder
- Flutter 강좌
- Image.network
- Flutter 예제
- Scaffold
- Snackbar
- HTTP
- Flutter Example
- 반석천
- InkWell
- Flutter 앱 배포
- Load Image
- Networking
- Flutter Tutorial
- Row
- listview
- node.js
- ListView.builder
- ListTile
- Row Widget
- Column Widget
- Hello World
- CrossAxisAlignment
- flutter
- AppBar
- WillPopScope
- navigator
- MainAxisAlignment
- Cached Image
- sqlite
- Today
- Total
꿈꾸는 시스템 디자이너
Flutter 강좌 - Provider 사용법 | How to use Flutter Provider 본문
Flutter 강좌 - Provider 사용법 | How to use Flutter Provider
독행소년 2019. 10. 31. 14:43Flutter Code Examples 강좌를 추천합니다.
- 제 블로그에서 Flutter Code Examples 프로젝트를 시작합니다.
- Flutter의 다양한 예제를 소스코드와 실행화면으로 제공합니다.
- 또한 모든 예제는 Flutter Code Examples 앱을 통해 테스트 가능합니다.
Flutter Code Examples 강좌로 메뉴로 이동
Flutter Code Examples 강좌 목록 페이지로 이동
Flutter Code Examples 앱 설치 | Google Play Store로 이동
Flutter Code Examples - Google Play 앱
Are you a beginner at Flutter? Check out the various features of Flutter through the demo. Source code for all demos is also provided.
play.google.com
Flutter 강좌 시즌2 목록 : https://here4you.tistory.com/149
이번 강좌에서는 최근 Google Flutter에서 소개한 Provider의 개념에 대해서 알아본다.
이번 강좌를 이해하기 위해선 기존의 StatefullWidget과 StatelessWidget에 대한 이해가 필요하다.
2019/10/25 - [Development/Flutter] - Flutter 강좌 - StatelessWidget과 StatefulWidget의 차이점과 사용법
Flutter 강좌 - StatelessWidget과 StatefulWidget의 차이점과 사용법
Flutter Code Examples 강좌를 추천합니다. 제 블로그에서 Flutter Code Examples 프로젝트를 시작합니다. Flutter의 다양한 예제를 소스코드와 실행화면으로 제공합니다. 또한 모든 예제는 Flutter Code Examples..
here4you.tistory.com
앱을 개발하다 보면 여러 개의 화면을 구성하게 되고 그 화면의 이동 간에 데이터를 공유하는 일이 빈번히 일어난다. 예를 들어 로그인 기능이 있는 앱에서 각 화면의 한켠에 사용자의 이름을 표시하고자 하려면 화면 페이지 이동마다 사용자의 이름을 전달하거나 static 인스턴스를 생성해서 데이터를 공유해야 한다. 이러한 기존의 방식은 코드를 복잡하게 한다. 또한 그 데이터의 변동이 발생할 경우 상태(State)의 업데이트를 통보하기도 쉽지 않다.
최근 소개된 Provider는 앱을 구성하는 모든 화면에서 데이터의 공유가 가능하게 하고 더 나아가 데이터의 변경이 발생하였을 시 해당 데이터를 참조하는 화면 구성에게도 통보가 가능하다.
우선 다음의 화면을 보자.

화면에는 사용자에 이름(Park)과 그 사용자의 통장 잔고(0원)를 출력하고 있다. 이 사용자의 이름과 잔고를 새로운 화면으로 전달하고자 한다.
다음 화면은 새로운 페이지를 로딩하고 사용자의 이름과 잔고를 출력하며, 버튼을 통해 잔고를 가감한 후 원래 페이지로 돌아갔을 때 변경된 잔고가 반영되는 것을 나타내고 있다.

위의 예제에서는 사용자의 이름과 잔고 데이터를 두 개의 페이지에서 서로 공유하고 있다. 특히 잔고의 경우 그 값이 변경되고 있으며 변경된 값이 각 화면 페이지 상태로 반영되고 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다. 이렇게 앱을 구성하는 복수의 화면에서 데이터를 공유할 수 있게 하는 것이 Provider의 기능이다.
그럼 이제 사용법을 알아보자.
1. 페키지 추가
Provider를 사용하기 위해 pubspec.yaml 파일에 Provider 플러그인을 추가한다.
dependencies:
provider: ^3.1.0+1
2. BankAccount 클래스 구현
통장 잔고에 해당하는 클래스인 BankAccount 클래스를 다음과 같이 구현한다.
class BankAccount with ChangeNotifier {
int _balance = 0;
int getBalance() => _balance;
void increment(int value) {
_balance += value;
notifyListeners(); //must be inserted
}
void decrement(int value) {
_balance -= value;
notifyListeners(); //must be inserted
}
}소스의 내용을 보면 잔고에 해당하는 필드인 _balance가 존재하고 그 값을 가감하기 위한 메서드가 두 개 존재한다. 여기서 중요한 것은 with 키워드를 통해 ChangeNotifier 클래스를 mixin 한다는 것이다. 일단 위 코드에서는 with 대신 extends 키워드를 사용해도 무방하다.
with와 extends의 차이는향 후 다시 다루도록 한다.
또 한가지 중요한 점은 _balance의 값을 변경할 경우 notifyListeners 메서드를 꼭 호출해줘야 한다는 것이다. notifyListeners 메서드는 ChangeNotifier 클래스에서 제공하며 해당 클래스의 인스턴스를 참조하는 화면(StatelessWidget 혹은 StatefulWidget)에 상태 변경을 통보하는 역할을 한다.
3. Provider 구현
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MultiProvider(
providers: [
ChangeNotifierProvider<BankAccount>(builder: (_) => BankAccount()),
Provider<String>.value(value: "Park")
],
child: MaterialApp(
title: "Provider Test",
home: HomePage(),
),
);
}
}Provider는 앱을 구성하는 모든 화면에서 사용할 수 있으므로 앱의 가장 큰 단위인 MaterialApp을 감싸는 방식으로 구현한다.
기존의 앱들이 MaterialApp에서 시작했던 것과는 달리 MaterialApp을 child로 가지는 Provider로 앱을 시작하는 것이다. 또한 앱에서는 복수의 Provider를 이용할수 있으며 이 경우 MultiProvider를 이용한다.
위 코드에서는 MultiProvider로 앱을 시작하고 있으며 사용할 Provider들을 rpviders 항목으로 등록하고 있다.
첫번째 Provider는 사용자의 잔고를 구현한 BankAccount 클래스이며, 두 번째 Provider는 사용자의 이름을 저장하는 String 타입의 값을 등록하고 있다.
잔고의 경우 가감이 발생하며 그 가감 발생시 상태변화로 반영되어야 하므로 ChangeNotifierProvider로 등록하고, 사용자의 이름의 경우 한번 등록 후 변경이 발생하지 않음으로 일반 Provider로 등록한 것이다.
MultiProvider의 child 항목에서 MaterialApp을 등록하여 HomePage 화면 클래스를 호출하는 형태이다.
4. 첫번째 화면(사용자 정보) 구현
class HomePage extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
BankAccount bankAccount = Provider.of<BankAccount>(context);
String name = Provider.of<String>(context);
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text("Provider Test")),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Text("Your Name is '$name'"),
Text("Your balance is ${bankAccount.getBalance()}"),
RaisedButton(
child: Text("Test with StatefulWidget"),
onPressed: () {
Navigator.push(context,
MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context) => TestSFW()));
},
),
RaisedButton(
child: Text("Test with StatelessWifet"),
onPressed: () {
Navigator.push(context,
MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context) => TestSLW()));
},
),
],
),
),
);
}
}첫 번째 화면에서는 사용자의 이름과 잔고를 출력하는 두 개의 Text 위젯과, 잔고를 가감할 수 있는 페이지로 이동하기 위한 두 개의 RaisedButton으로 구성되고 있다.
사용자의 이름과 잔고를 참조하기 위해서는 MultiProvider에 등록한 Provider의 Consumer를 이용하며 다음과 같은 형식으로 참조 가능하다.
var consumer = Provider.of<Type>(context);위의 방식으로 bankAccount와 name 필드를 생성해서 두 Text 위젯에 연결하고 이다.
실행화면은 이미 위에서 본것과 동일하다.

5. 두번째 화면(잔고 가감) 구현(StatefulWidget 방식)
class TestSFW extends StatefulWidget {
@override
TestSFWState createState() => TestSFWState();
}
class TestSFWState extends State<TestSFW> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
BankAccount bankAccount = Provider.of<BankAccount>(context);
String name = Provider.of<String>(context);
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text("SFW with Prodiver")),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Text("Your Name is '$name'"),
Text("Your balance is ${bankAccount.getBalance()}"),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("+1"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.increment(1);
},
),
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("+10"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.increment(10);
},
),
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("+100"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.increment(100);
},
),
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("-1"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.decrement(1);
},
),
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("-10"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.decrement(10);
},
),
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("-100"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.decrement(100);
},
),
].map(
(child) {
return Container(
margin: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 5),
width: 40,
child: child,
);
},
).toList(),
)
],
),
),
);
}
}코드의 구성은 단순하다. 사용자의 이름과 잔고를 참조하기 위해 Consumer 필드 두 개(bankAccount, name)를 생성하고, 이를 Text 위젯에 연결하였다.
잔고를 가감하기 위해 각 버튼의 onPressed 속성에서 increment 메서드와 decrement 메서드를 호출하고 있다.
화면을 실행하여 버튼을 통해 테스트를 해보자.
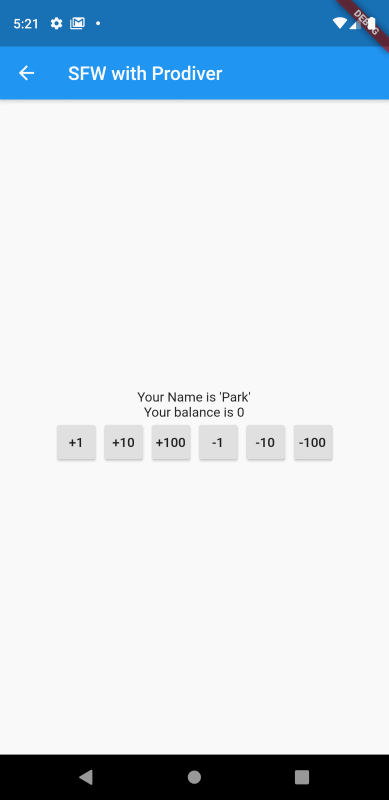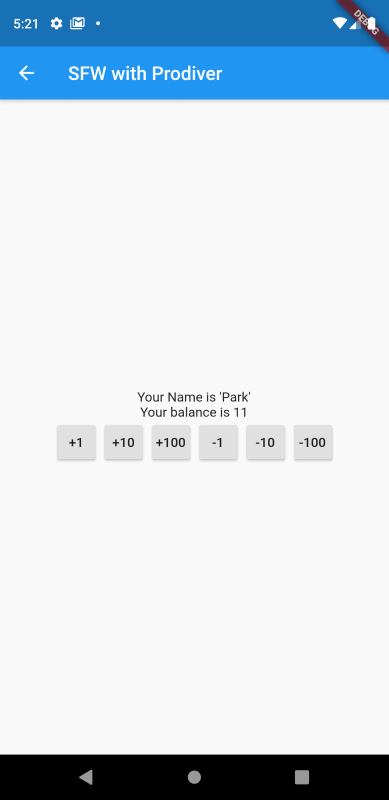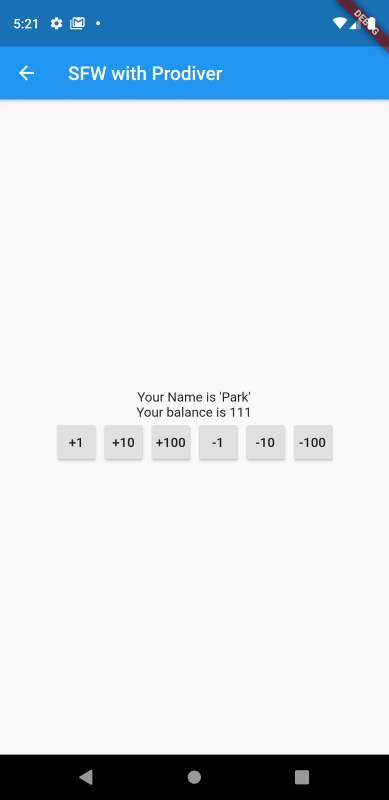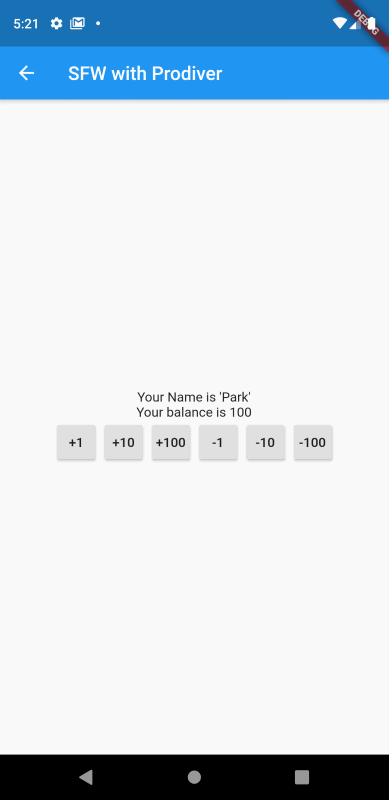
버튼을 클릭할 때마다 값이 변경되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
여기서 한가지 생각해볼 점이 있다. 기존 StatefulWidget의 강좌에서도 비슷하게 값을 가감하는 화면을 개발했었다. 그때와의 차이점이 무엇일까?
바로 setState 메서드를 이용하지 않았음에도 상태값(잔고)이 실시간으로 반영되고 있다는 것이다.
그 이유는 잔고(_balance)를 가감하는 메서드에서 notifyListeners 메서드를 호출하도록 BankAccount 클래스를 구현했기 때문이다. notifyListeners 메서드에 의해 _balance를 참조하는 모든 화면의 구성이 자동으로 업데이트되고 있는 것이다.
각 화면에서 상태를 변경할 때마다 setState 메서드를 이용해서 직접 상태를 변경하는 부담이 Provider를 이용함으로써 해결되고 있다.
원래 화면으로 돌아가서 변경한 잔고의 값이 정상 출력되고 있는 것을 확인하자.
6. 또다른 두 번째 화면(잔고 가감) 구현(StatelessWidget 방식)
StatefulWidget 기반으로 Provider를 이용해선 코드를 SatelessWidget 방식으로도 구현해보자. build 메서드 내부의 코드는 AppBar의 테스트만을 제외하고 완벽하게 동일하다.
class TestSLW extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
BankAccount bankAccount = Provider.of<BankAccount>(context);
String name = Provider.of<String>(context);
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text("SFW with Provider")),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Text("Your Name is '$name'"),
Text("Your balance is ${bankAccount.getBalance()}"),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("+1"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.increment(1);
},
),
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("+10"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.increment(10);
},
),
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("+100"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.increment(100);
},
),
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("-1"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.decrement(1);
},
),
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("-10"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.decrement(10);
},
),
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("-100"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.decrement(100);
},
),
].map(
(child) {
return Container(
margin: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 5),
width: 40,
child: child,
);
},
).toList(),
)
],
),
),
);
}
}
그럼 해당 화면을 실행시켜 테스트를 해보자.
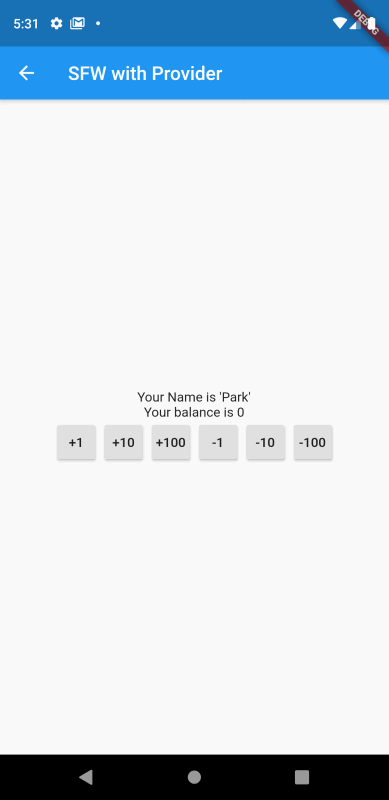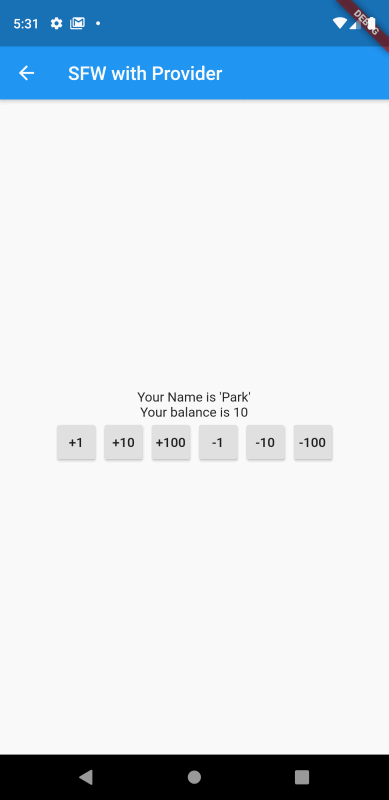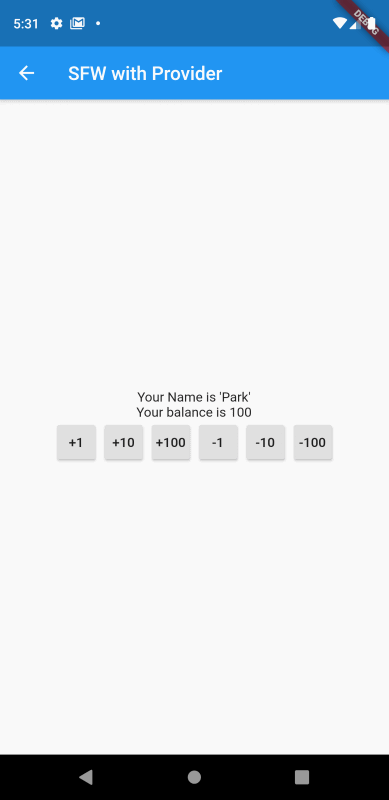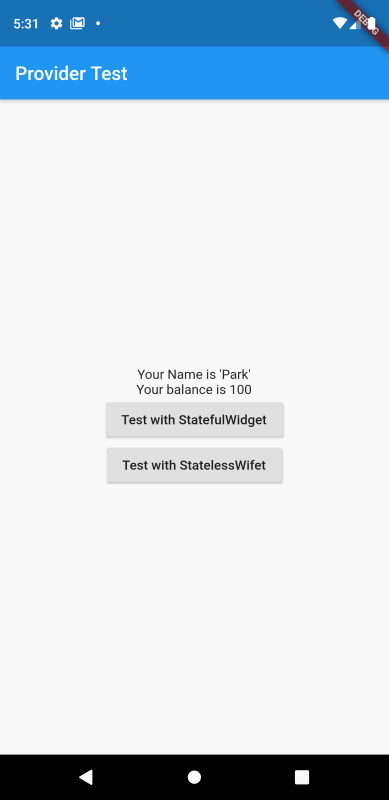
위의 경우도 StatefullWidget 기반의 코드와 동일하게 잔고의 값이 화면상에 실시간으로 반영되고 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
기존 강의에서 StatelessWidget의 경우 상태를 가지지 않으므로 화면이 한번 구성된 후에는 화면이 사라질 때까지 변경되지 않으며 build 메서드도 화면이 생성될 때 한 번만 호출된다고 했었다.
위 코드에서 build 메서드에 print문을 추가한 후 화면의 버튼들을 클릭해보자.
Performing hot reload...
Syncing files to device Android SDK built for x86...
Reloaded 1 of 478 libraries in 247ms.
I/flutter (10833): build method of TestSLW
I/flutter (10833): build method of TestSLW
I/flutter (10833): build method of TestSLW
I/flutter (10833): build method of TestSLW
I/flutter (10833): build method of TestSLW화면상의 버튼을 클릭하면 위의 로그와 같이 build 메서드가 호출되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
정리하면, Provider를 이용하면 StatelessWidget으로 구성된 화면도 상태를 가지며 상태변경시 build 메서드가 호출되어 화면이 재구성된다는 것을 확인할 수 있다. Provider를 이용하며 Flutter의 StatefulWidget과 StatelessWidget의 경계가 허물어진다는 것을 의미하기도 한다.
7. 결론
- Provider는 앱을 구성하는 모든 화면에서 참조가 가능한 공통의 데이터를 생성/관리할 때 유용하다.
- 정적인 데이터라면 Provider를 이용하고, 변경이 가능한 데이터라면 ChangeNotifierProvider를 이용한다.
- ChangeNotifierProvider로 등록된 데이터를 참조하는 경우 그 화면이 StatelessWidget으로 구성되었어도 데이터 변경이 build 메서드가 재호출 되어 화면이 재구성된다.
8. 전체 소스코드
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:provider/provider.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class BankAccount with ChangeNotifier {
int _balance = 0;
int getBalance() => _balance;
void increment(int value) {
_balance += value;
notifyListeners(); //must be inserted
}
void decrement(int value) {
_balance -= value;
notifyListeners(); //must be inserted
}
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MultiProvider(
providers: [
ChangeNotifierProvider<BankAccount>(builder: (_) => BankAccount()),
Provider<String>.value(value: "Park")
],
child: MaterialApp(
title: "Provider Test",
home: HomePage(),
),
);
}
}
class HomePage extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
BankAccount bankAccount = Provider.of<BankAccount>(context);
String name = Provider.of<String>(context);
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text("Provider Test")),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Text("Your Name is '$name'"),
Text("Your balance is ${bankAccount.getBalance()}"),
RaisedButton(
child: Text("Test with StatefulWidget"),
onPressed: () {
Navigator.push(context,
MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context) => TestSFW()));
},
),
RaisedButton(
child: Text("Test with StatelessWifet"),
onPressed: () {
Navigator.push(context,
MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context) => TestSLW()));
},
),
],
),
),
);
}
}
class TestSFW extends StatefulWidget {
@override
TestSFWState createState() => TestSFWState();
}
class TestSFWState extends State<TestSFW> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
BankAccount bankAccount = Provider.of<BankAccount>(context);
String name = Provider.of<String>(context);
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text("SFW with Prodiver")),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Text("Your Name is '$name'"),
Text("Your balance is ${bankAccount.getBalance()}"),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("+1"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.increment(1);
},
),
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("+10"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.increment(10);
},
),
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("+100"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.increment(100);
},
),
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("-1"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.decrement(1);
},
),
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("-10"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.decrement(10);
},
),
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("-100"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.decrement(100);
},
),
].map(
(child) {
return Container(
margin: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 5),
width: 40,
child: child,
);
},
).toList(),
)
],
),
),
);
}
}
class TestSLW extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
BankAccount bankAccount = Provider.of<BankAccount>(context);
String name = Provider.of<String>(context);
print("build method of TestSLW");
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text("SFW with Provider")),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Text("Your Name is '$name'"),
Text("Your balance is ${bankAccount.getBalance()}"),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("+1"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.increment(1);
},
),
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("+10"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.increment(10);
},
),
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("+100"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.increment(100);
},
),
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("-1"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.decrement(1);
},
),
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("-10"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.decrement(10);
},
),
RaisedButton(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Text("-100"),
onPressed: () {
bankAccount.decrement(100);
},
),
].map(
(child) {
return Container(
margin: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 5),
width: 40,
child: child,
);
},
).toList(),
)
],
),
),
);
}
}'Development > Flutter' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Flutter 강좌 - [Firebase] 구글 로그인(Google Sign in) 사용법 (2) | 2019.11.04 |
|---|---|
| Flutter 강좌 - [Firebase] Firebase 연동 방법 (6) | 2019.11.01 |
| Flutter 강좌 - StatelessWidget과 StatefulWidget의 차이점과 사용법 (6) | 2019.10.25 |
| Flutter 강좌 - 앱 배포하기 후기 | 구글마켓등록시간 (6) | 2019.10.23 |
| Flutter 강좌 - 앱 배포하기 2/2 | 마켓(구글 플레이)에 앱 등록 (0) | 2019.10.10 |




